Annotations Java

Annotations
Versions [{“Name”:“Java SE 5”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 6”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 7”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 8”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 9 (Early Access)”,“Gr...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Annotations
Annotations Annotations have a number of uses, among them: Information for the compiler — Annotations can be used by the compiler to detect errors or suppress warnings. Compile-time and deployment-ti...
📚 Read more at Learn Java🔎 Find similar documents

The idea behind Annotations
The Java Language Specification describes Annotations as follows: An annotation is a marker which associates information with a program construct, but has no effect at run time. Annotations may appear...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Java Annotations 101
Learn about the primary Java annotations and how to use them🍎 If you have ever seen a Java codebase, there is a high chance you saw something like @Override or similar tags before a method or class. ...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Reading Annotations
Annotations are widely used with the Reflection API. Many frameworks use them extensively and with great success. This is the case for the object relational mapping frameworks, the dependency Injecti...
📚 Read more at Learn Java🔎 Find similar documents

Mastering Annotations: From Basics to Advanced Techniques
Annotations in Java Annotations in Java serve as powerful metadata markers, enriching your code with additional information. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting your journey, understa...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents
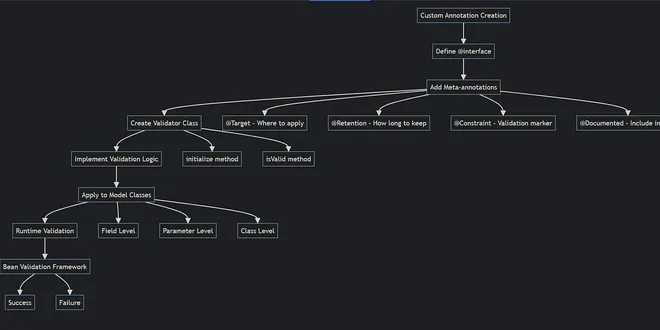
How to Write Custom Java Annotations: A Complete Guide with Real-World Validation Example
Java annotations provide a powerful way to add metadata to your code, enabling declarative programming patterns and reducing boilerplate… Continue reading on Javarevisited
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Annotations
Declaration annotations should be put on a separate line from the declaration being annotated. @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public T[] toArray(T[] typeHolder) { ... } However, few or short annotatio...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents
JPA Annotations Overview
Java Persistence API (JPA) annotations are a set of annotations provided by the JPA specification, which is part of the Java EE (Enterprise Edition) standard.These annotations are used to configure an...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents
Processing Java Annotations at compilation time
Java annotations can be used for storing metadata that would have an impact on how the programs would be executed. Apart from the annotations that are available in Java, you can write your own Custom ...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents
Compile Time Annotation Processing in Java
Java annotations have quietly become one of the most transformative features in the language. While they may seem like simple markers or metadata, annotations can actually drive entire frameworks, sim...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Java: Creating and Using Custom Annotations
🍎 In my previous article, I explained what annotations are and how to use prebuilt annotations in Java. Java also gives us the option to create our own annotations to enhance our code. To generate an...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents


