Asyncio Task&Futures

concurrent.futures.Future vs asyncio.Future
The Python standard library provides two Future classes. The first is in the concurrent.futures module and the second is in the asyncio module: This raises the question: What is the difference between...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents

What is an Asyncio Task
You can create Task objects from coroutines in asyncio programs. Tasks provide a handle on independently scheduled and running coroutines and allow the task to be queried, canceled, and results and ex...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents

Asyncio Concurrent Tasks
We can execute asyncio tasks and coroutines concurrently, a main benefit of using asyncio. There are four main ways that we can achieve this, including issuing coroutines as independent tasks and awai...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents

concurrent.futures.Future and asyncio.Future Not Compatible
You can mix concurrent.futures.Future and asyncio.Future objects in your Python program because they are not compatible. This means that instances of the asyncio.Future class cannot be used in concurr...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents
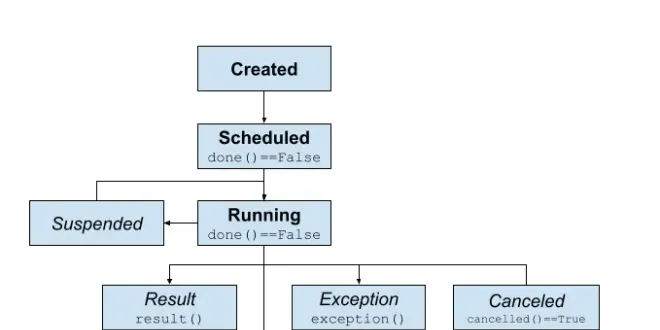
Asyncio Task Life-Cycle
An asyncio task has a 4-part life-cycle that transitions from created, scheduled, running, and done. In this tutorial, you will discover the life-cycle of an asyncio Task in Python. Let’s get started....
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents

What is an Asyncio Pending Task
A task that is scheduled or suspended will be assigned an internal state of “pending“. In this tutorial, you will discover pending asyncio tasks in Python. Let’s get started. What is an Asyncio Task A...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents

Asyncio Disappearing Task Bug
Last Updated on December 11, 2023 You can have running background tasks in asyncio suddenly disappear. This is a known bug and can be avoided by ensuring that you keep a strong reference to all tasks ...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents

Asyncio Suspend Forever
The asyncio.Server in the asyncio module provides a way to suspend the main coroutine forever and accept client connections. Reviewing the code in the standard library, we can see that this is achieve...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents

How to Create Asyncio Tasks in Python
You can create a task from a coroutine using the asyncio.create_task() function, or via low-level API functions such as asyncio.ensure_future() and loop.create_task(). In this tutorial, you will disco...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents

How to Get the Current Asyncio Task in Python
You can get the current task via asyncio.current_task() function. In this tutorial, you will discover how to get and use the current asyncio task in Python. Let’s get started. What is an Asyncio Task ...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents

Asyncio Task Cancellation Best Practices
Last Updated on December 20, 2023 Tasks in asyncio can be canceled manually and automatically. Therefore, we must develop asyncio programs with the expectation that our custom tasks may be canceled at...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents

When Are Asyncio Tasks Canceled
Last Updated on December 18, 2023 Asyncio tasks can be canceled at any time. Asyncio tasks can be canceled manually while they are scheduled or running. Additionally, tasks can be automatically cancel...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents


