BufferedReader BufferedWriter

BufferedWriter
Versions [{“Name”:“Java SE 1.1”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 1.2”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 1.3”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 1.4”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 5”,“GroupName...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

BufferedReader
Introduction The BufferedReader class is a wrapper for other Reader classes that serves two main purposes: A BufferedReader provides buffering for the wrapped Reader . This allows an application to re...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents
How To Read Text File With BufferedReader In Java
BufferedReader class is one of the most used when it comes to read Text files in Java.This class provides methods that can read characters from input stream. As name says it buffers read characters he...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

StringWriter Example
Java StringWriter class is a character stream that collects output from string buffer, which can be used to construct a string. The StringWriter class extends the Writer class. In StringWriter class, ...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

FileReader and FileWriter in Java: Simplified File Handling
Photo by Drew Coffman on Unsplash In Java, file handling is a fundamental aspect of many applications, especially when dealing with text-based data. In our previous article, we explored FileInputStrea...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Understanding BufferedInputStream and BufferedOutputStream in Java
Photo by Ries Bosch on Unsplash In Java, file handling often involves enhancing the efficiency of input and output operations. While FileInputStream and FileOutputStream are excellent for basic file I...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Pitfall - Small reads writes on unbuffered streams are inefficient
Consider the following code to copy one file to another: import java.io.*; public class FileCopy { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream(a...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Reading a file using Channel and Buffer
Channel uses a Buffer to read/write data. A buffer is a fixed sized container where we can write a block of data at once. Channel is a quite faster than stream-based I/O. To read data from a file usin...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

ByteBuffer
Introduction The ByteBuffer class was introduced in java 1.4 to ease working on binary data. It’s especially suited to use with primitive type data. It allows the creation, but also subsequent manipul...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Readers and Writers
Versions [{“Name”:“Java SE 1.1”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 1.2”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 1.3”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 1.4”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 5”,“GroupName...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents
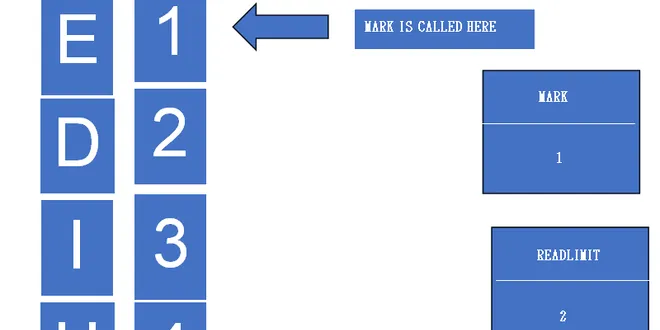
InputStreams- Rereading and Concatenating operations
Rereading InputStreams Java InputStream specifically large streams can be tricky to handle as they can only be read once. One apparent approach to mitigate this is to read them into a byte array and t...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

StringBuffer
Introduction Introduction to Java StringBuffer class.
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents


