Comparable vs Comparator

Comparable vs Comparator Simplified - A Must-Read for Interviews!
✅ Comparable and Comparator are two ways to achieve this. Understanding their differences and knowing when to use which is essential for cracking Java interviews. In almost every Java interview , you’...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Comparable and Comparator
Versions [{“Name”:“Java SE 1.2”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 1.3”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 1.4”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 5”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 6”,“GroupName”:...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Explain the Comparator and Comparable interfaces
Sorting is one of the crucial aspect when we are developing any application. When you are dealing with price or marks etc, we usually use Int or double as data type but what if you are working with cu...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents
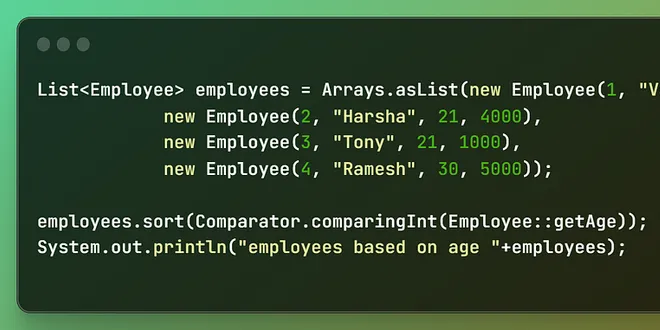
You don’t know Comparators in-practice, Do You?
9 ways you can use Comparators to solve problems When I started learning about sorting objects in Java, I was bored with the interviewer’s favourite question—Comparable vs. Comparator. So, I thought ...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

The compareTo and compare Methods
The Comparable<T interface requires one method: public interface Comparable<T { public int compareTo(T other); } And the Comparator<T interface requires one method: public interface Comparator<T { pub...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Writing and Combining Comparators
Implementing a Comparator with a Lambda Expression Thanks to the definition of functional interfaces, the good old Comparator<T interface introduced in JDK 2 became functional. So, implementing a com...
📚 Read more at Learn Java🔎 Find similar documents

Java Comparator interface
To order a collection of objects, Java provides the Comparable and Comparator interfaces. In the previous tutorial, I demonstrated with examples how to use the Comparable interface. In this tutorial,...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Natural comparable vs explicit comparator sorting
There are two Collections.sort() methods: One that takes a List<T as a parameter where T must implement Comparable and override the compareTo() method that determines sort order. One that takes a List...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents
Comparator Vs Comparable In Java
As a Java Developer we always come Across these two Interfaces when we need to sort any custom Object ,lets discuss its use cases:-
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Creating a Comparator using comparing method
Comparator.comparing(Person::getName) This creates a comparator for the class Person that uses this person name as the comparison source. Also it is possible to use method version to compare long, int...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Java Comparable interface
The Java language frequently operates on objects, and often, these objects need to be ordered in some way, such as by date. To order objects, we must compare them and determine which ones are greater...
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

Write Efficient Bug-free and Simple Comparators in Java - JEP Café #17
Comparator are elements used daily in all Java applications. There are fairly easy to write, but must also follow several subtle rules. This JEP Café explains all of them: how to leverage the factory...
📚 Read more at Inside Java🔎 Find similar documents


