Functional Interfaces

Functional Interfaces
Introduction In Java 8+, a functional interface is an interface that has just one abstract method (aside from the methods of Object). See JLS §9.8. Functional Interfaces .
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents
Functional Interfaces: The Hidden Bridge Between OOP and FP in Java..
🌱 What is a Functional Interface? A functional interface is an interface that has exactly one abstract method (a.k.a. SAM — Single Abstract Method). Examples you already know: Runnable (run)
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents
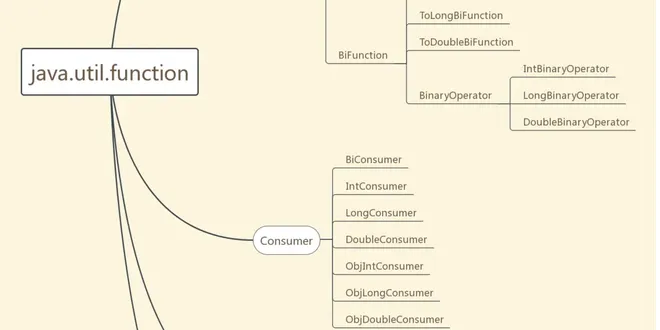
Functional Interface vs @FunctionalInterface
Introduction The functional interface is an interface that contains only one abstract method . You can use lambda expressions to create instances of this interface.
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Understand functional interfaces
In Java 8 the @FunctionalInterface annotation was introduced, allowing API developers to designate that a particular class is intended for use in lambda expressions. It is not necessary that a class h...
📚 Read more at Java Best Practices🔎 Find similar documents

Understand functional interfaces
In Java 8 the @FunctionalInterface annotation was introduced, allowing API developers to designate that a particular class is intended for use in lambda expressions. It is not necessary that a class ...
📚 Read more at Java Best Practices🔎 Find similar documents
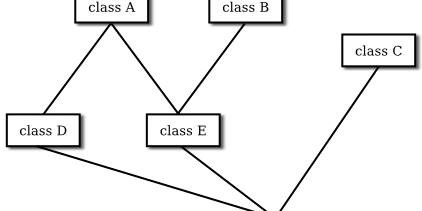
Interfaces
Section 5.7 Interfaces Some object-oriented programming languages, such as C++, allow a class to extend two or more superclasses. This is called multiple inheritance . In the illustration below, for e...
📚 Read more at Introduction to Programming Using Java🔎 Find similar documents

Java Functional Interfaces For the Impatient: Part 1
In this article, we will learn about Java Functional Interfaces with coding examples. This is just part one of the series as I will try to cover the main functional interfaces which come under Packag...
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

Java Functional Interface and Lamda Implementation
A functional interface in Java is an interface that contains only a single abstract (unimplemented) method. A functional interface may have defaulted, and static methods may have an implementation…
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

Interfaces
Introduction An interface is a reference type, similar to a class, which can be declared by using interface keyword. Interfaces can contain only constants, method signatures, default methods, static m...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents
Functional Java 1 — Functional Interfaces
Java 8 is undoubtedly one of the most significant releases in Java history. While Java remains an inherently object-oriented language, the introduction of core functional features has brought a breath...
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

Interfaces
Interfaces in Java There are a number of situations in software engineering when it is important for disparate groups of programmers to agree to a "contract" that spells out how their software intera...
📚 Read more at Learn Java🔎 Find similar documents

List of standard Java Runtime Library functional interfaces by signature
Parameter Types | Return Type | Interface | –––––––– | ———– | ——— | () | void | Runnable | () | T | Supplier | () | boolean | BooleanSupplier | () | int | IntSupplier | () | long | LongSupplier | () |...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents


