Interfaces

Interfaces
Introduction An interface is a reference type, similar to a class, which can be declared by using interface keyword. Interfaces can contain only constants, method signatures, default methods, static m...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Interfaces
Interfaces in Java There are a number of situations in software engineering when it is important for disparate groups of programmers to agree to a "contract" that spells out how their software intera...
📚 Read more at Learn Java🔎 Find similar documents

1.2 Interfaces
An interface , sometimes also called an abstract data type , defines the set of operations supported by a data structure and the semantics, or meaning, of those operations. An interface tells us nothi...
📚 Read more at Open Data Structures in Java🔎 Find similar documents
Interfaces
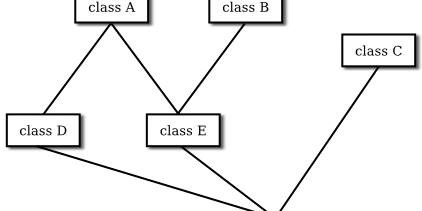
Section 5.7 Interfaces Some object-oriented programming languages, such as C++, allow a class to extend two or more superclasses. This is called multiple inheritance . In the illustration below, for e...
📚 Read more at Introduction to Programming Using Java🔎 Find similar documents

Marker Interfaces
When programming in Java, it is always advisable to program to the interface and not to the realisation. Interfaces are programming constructs that allow us to hide the real implementation detail of o...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Implementing Interfaces With Golang
Interfaces are tools to define sets of actions and behaviors. They help objects to rely on abstractions and not on concrete implementations of other objects. We can compose different behaviors by…
📚 Read more at Better Programming🔎 Find similar documents

Functional Interfaces
Introduction In Java 8+, a functional interface is an interface that has just one abstract method (aside from the methods of Object). See JLS §9.8. Functional Interfaces .
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents
Data is the New Interface
From the previous chapters, we learned that interfaces exist at different scales in our artificial reality; interface designers internalize technological, ideological, and economic realities of…
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

Usefulness of interfaces
Interfaces can be extremely helpful in many cases. For example, say you had a list of animals and you wanted to loop through the list, each printing the sound they make. {cat, dog, bird} One way to do...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents
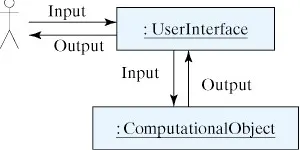
The User Interface
Section 4.2 The User Interface The user interface is that part of the program that handles the input and output interactions between the user and the program. As an interface, it limits or constrains ...
📚 Read more at Java Java Java: Object-Oriented Problem Solving🔎 Find similar documents

The „I“ in SOLID Software Architecture — Interface Segregation Principle
In software architecture interfaces are contracts that define no behaviour themself but that other modules must adhere to. They allow the consumer of a module to know how to talk to the module…
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

Interface members
public interface MyInterface { public void foo(); int bar(); public String TEXT = "Hello"; int ANSWER = 42; public class X { } class Y { } } Interface members always have public visibility, even if th...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents


