Microservices Principles

Principles of Microservice Architecture
ENGINEERING AT SCALE The Day the Monolith Cracked: Why We Finally Embraced Microservices. 🔑 Key Principles of Designing a Microservices Architecture :- Designing a microservices-based system require...
📚 Read more at Towards AI🔎 Find similar documents
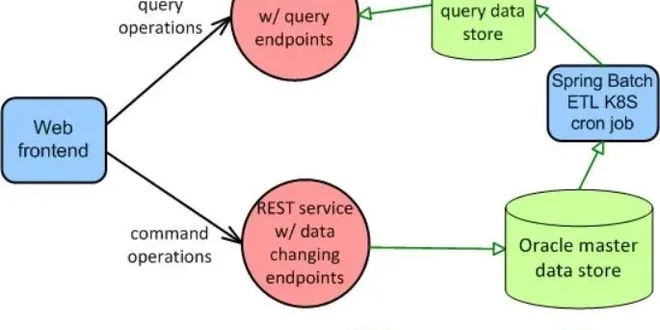
Microservices are Mess Without These Design Principles and Best Practices
Designing Microservices for your organization? Follow these design principles to create robust and scalable Microservices
📚 Read more at Javarevisited Newsletter🔎 Find similar documents

Ace Your Microservices Interviews
Microservices represent a paradigm shift in software architecture, breaking down applications into small, independently deployable services. This approach offers unparalleled flexibility in scaling an...
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents
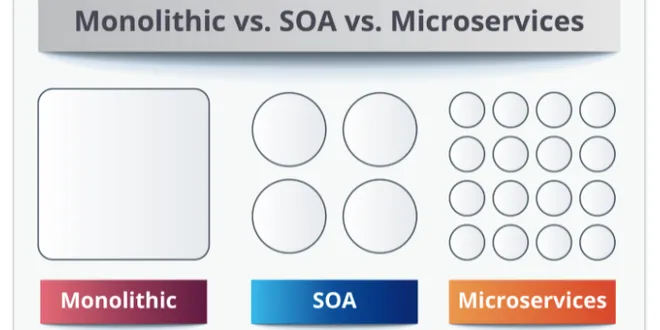
Principles of the Microservice Architecture
The Microservice Architecture is a design paradigm where a large complex application is broken down into a suite of small function component services that have the following characteristics: The…
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

Microservices
As the name suggests, microservices is a software development pattern where an application is split as a collection of loosely-coupled services that communicate using lightweight protocols. The micros...
📚 Read more at Software Architecture with C plus plus🔎 Find similar documents

The IDEALS Principles Every Microservice Developer Should Know
Learn the IDEALS design principles. Every microservice developer should have these principles in mind while developing microservice-based applications.
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

Microservices Best Practices for Developers
Photo by Growtika on Unsplash Microservice is a widely accepted phenomenon for software development. Using this approach, businesses can gain an advantage in a highly competitive market. By collaborat...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents
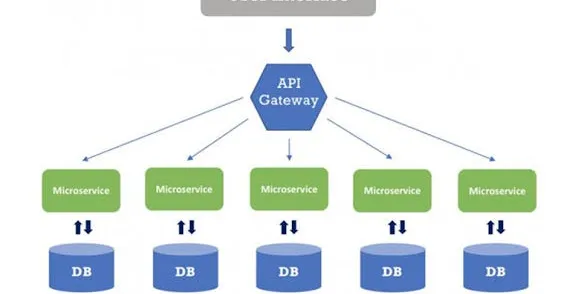
Top 10 Microservices Design Patterns and Principles (with Examples)
Microservices architecture are mess without these patterns
📚 Read more at Javarevisited Newsletter🔎 Find similar documents

Immersive guide to microservices
Let me present you main ideas around microservices architecture (short: MSA), which I learnt on the job and from this comeplling book: Building Microservices, 2nd Edition This article is not a study b...
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

Getting started with Microservices
A complete guide to Creation, Registry and Communication with Spring boot and MongoDB. Hey there! Recently delved into the world of microservices and discovered more invaluable insights. Inspired to ...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents
Characteristics of microservices
Since the microservice style is fairly recent, there is no single definition for microservices. According to Martin Fowler, there are several essential characteristics of microservices, which we will ...
📚 Read more at Software Architecture with C plus plus🔎 Find similar documents

5 Prerequisites To Know Before Adopting Microservices
Microservices is one most common architectural patterns to build highly scalable, distributed applications. This pattern describes delivering the system via small, independently releasable services…
📚 Read more at Better Programming🔎 Find similar documents


