Operators Java

Operators
Introduction Operators in Java programming language are special symbols that perform specific operations on one, two, or three operands, and then return a result. Remarks An operator is a symbol (or s...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Java Operators: Boost Your Coding Skills
Operators in Java are symbols used to perform various operations on operands, such as arithmetic, comparison, and logical operations. They are an essential part of the Java programming language.
📚 Read more at JavaToDev🔎 Find similar documents

Java Operators: With Great Power Comes Great Syntactic Confusion
A simple + , a modest = , maybe a sneaky && hiding in a condition. But don’t be fooled — these tiny symbols are where your Java code lives or dies . Operators are the unsung action heroes of your code...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Using Operators in Your Programs
Operators Now that you have learned how to declare and initialize variables, you probably want to know how to do something with them. Learning the operators of the Java programming language is a good...
📚 Read more at Learn Java🔎 Find similar documents
Java Data and Operators
Chapter 5 Java Data and Operators After studying this chapter, you will Objectives Understand the role that data play in effective program design. Be able to use all of Java’s primitive types and thei...
📚 Read more at Java Java Java: Object-Oriented Problem Solving🔎 Find similar documents
Java Essentials: Understanding Operators and the Binary Number System
Welcome to the 11th article of our comprehensive series designed to guide you through the nuances of Java programming. Today, we will focus on two pivotal concepts that form the bedrock of not just Ja...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Summary of Operators
Simple Assignment Operator Operator Description = Simple assignment operator Arithmetic Operators Operator Description + Additive operator (also used for String concatenation) - Subtraction operator ...
📚 Read more at Learn Java🔎 Find similar documents

The Arithmetic Operators -
The Java language provides 7 operators that perform arithmetic on integer and floating point values. There are two \+ operators: The binary addition operator adds one number to another one. (There is ...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Java Unary Operators in a Nutshell
Introduction J ava has introduced various types of operators to perform different kinds of operations which we need to do in our implementations. Unary operators are one of them that requires only one...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Operator Overloading in Java
In this post, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of operator overloading in Java. Although Java doesn’t natively support operator overloading, we’ll discover how Manifold can extend Java with that...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents
Operators
After seeing quite a few data types and some ways to convert them, it is time for the next major building block: operators. These come in handy whenever we want to work with the variables, modify them...
📚 Read more at JavaScript from Beginner to Professional🔎 Find similar documents
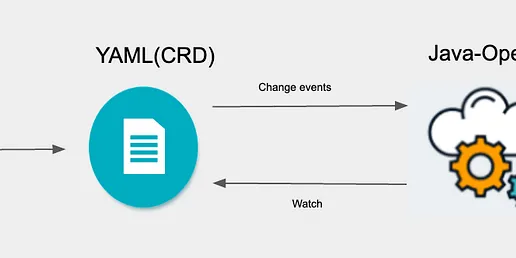
First Try on Java Operator SDK
Demo on java-operator-sdk and compare it with Kubebuilder Continue reading on Level Up Coding
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents


