Probability density function

Chapter 6 Probability density functions
The code for this chapter is in density.py . For information about downloading and working with this code, see Section 0.2 . 6.1 PDFs The derivative of a CDF is called a probability density function ,...
📚 Read more at Think Stats🔎 Find similar documents
Probability Mass and Density Functions
Probability mass and density functions are used to describe discrete and continuous probability distributions, respectively. This allows us to determine the probability of an observation being…
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents

What Is A Probability Density Function?
In the wonderful world of statistics, distributions are an absolutely vital component that sits at the center of a universe of mathematics. Distributions are used to describe data mathematically, and…...
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents

What Is A Cumulative Distribution Function?
Back in May, I took a look at a distribution function that belongs to most statistical distributions called the Probability Density Function, or PDF. The PDF is a very important part of statistical…
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents

Chapter 3 Probability mass functions
The code for this chapter is in probability.py . For information about downloading and working with this code, see Section 0.2 . 3.1 Pmfs Another way to represent a distribution is a probability mass ...
📚 Read more at Think Stats🔎 Find similar documents

How To Find Probability From Probability Density Plots
If you’ve been in data science field for quite some time, chances are you might have had made probability density plots (similar as below) to understand the overall distribution of your data. A…
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents
What Are The Odds? — Kernel Density Estimation
Often times, it can be incredibly useful to know the probability density function for a given set of observations. Unfortunately, most random samples of data will probably have unknown density…
📚 Read more at Analytics Vidhya🔎 Find similar documents

Statistical Distributions
A probability distribution is a mathematical function that provides the probabilities of the occurrence of various possible outcomes in an experiment. Probability distributions are used to define…
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents
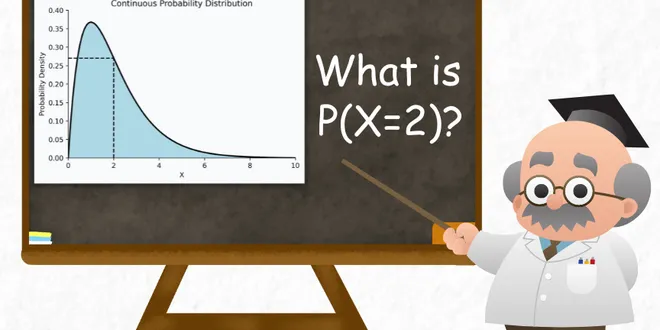
The Most Common Way a Continuous Probability Distribution is Misinterpreted
Consider the following probability density function of a continuous probability distribution. Say it represents the time one may take to travel from point A to B. For simplicity, we are assuming a uni...
📚 Read more at Daily Dose of Data Science🔎 Find similar documents

Probability & Statistics for Beginners in Machine Learning: Part 3 — Probability Distribution
A probability distribution is the mathematical function through which the probability of occurrence of different possible outcomes in an experiment can be calculated. Some very common examples we can…...
📚 Read more at Analytics Vidhya🔎 Find similar documents
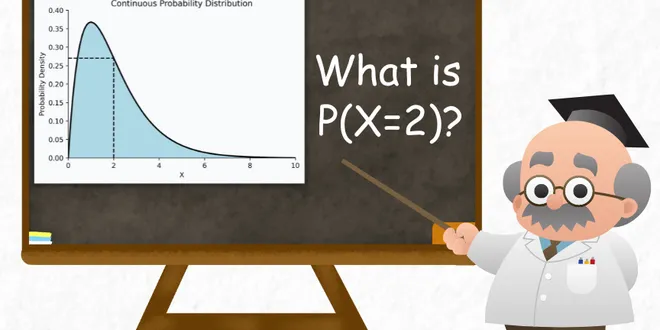
The Most Common Misconception About Continuous Probability Distributions
Let me ask you a question today. Consider the following probability density function of a continuous probability distribution. Say it represents the time one may take to travel from point A to B.
📚 Read more at Daily Dose of Data Science🔎 Find similar documents

Probability
Many machine learning methods are rooted in probability theory. Probabilistic methods in this book include linear regression , Bayesian regression , and generative classifiers . This section covers t...
📚 Read more at Machine Learning from Scratch Book🔎 Find similar documents


