R2
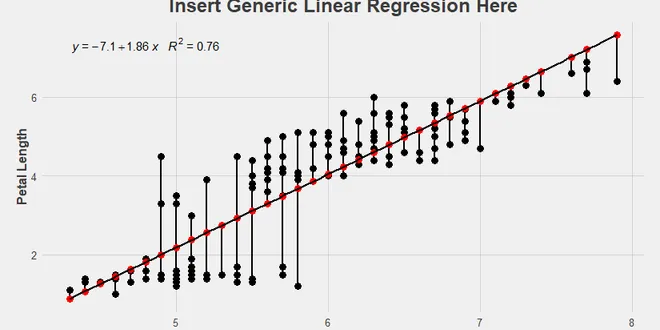
Moving Away From R²
R² is a well known model metric that every data analyst has in her toolbelt, but despite its prevalence, there is a mismatch between how data analysts tend to talk about and use this metric versus…
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents

Interpreting R²: a Narrative Guide for the Perplexed
An accessible walkthrough of fundamental properties of this popular, yet often misunderstood metric from a predictive modeling perspective Photo by Josh Rakower on Unsplash R² (R-squared), also known...
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents
What is R² score in Regression?
R-squared is a statistical measure that represents the goodness of fit. The R-squared score for a perfect fit of a regression model is 1. i.e, the model is fitted well as the r-squared value is close ...
📚 Read more at Python in Plain English🔎 Find similar documents
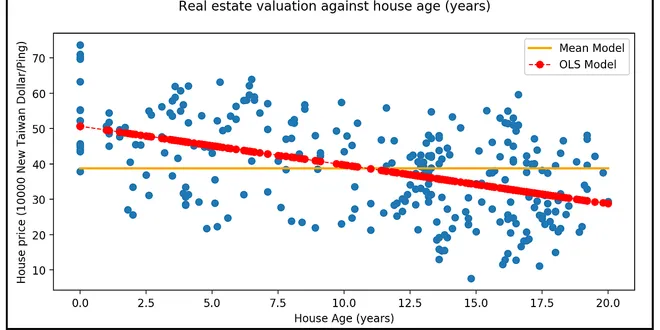
The Complete Guide to R-squared, Adjusted R-squared and Pseudo-R-squared
The technical definition of R² is that it is the proportion of variance in the response variable 'y' that your regression model is able to "explain" via the introduction of regression variables.
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents
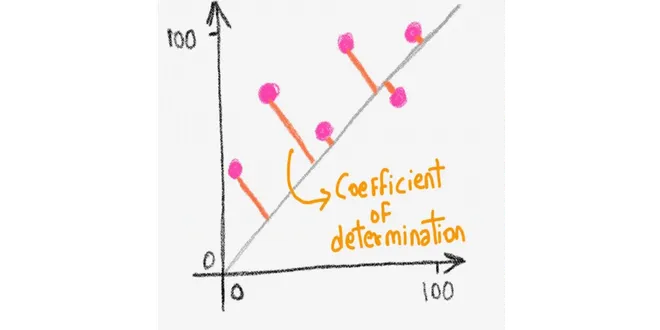
r² or R² — When to Use What
The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) is used to identify patterns in things whereas the coefficient of determination (R²) is used to identify the strength of a model.
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents
Data Science: Explaining R² in Statistics
R-squared is a metric of correlation. Correlation is measured by “r” and it tells us how strongly two variables can be related. A correlation closer to +1 means a strong relationship in the positive…
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents

R-Squared(R²)
Tutorial for calculating R² using Python with data provided from MacroTrends. Full working code provided to the reader. This article serves as a step by step tutorial for the R² method with full work...
📚 Read more at Python in Plain English🔎 Find similar documents

Explore R2 and Adjusted-R2 metrics intuitively
In this article, you will learn intuitively how R2 and Adjusted-R2 metrics work. Photo by Siora Photography on Unsplash R2 is widely used as an evaluation metric for regression machine learning tasks...
📚 Read more at Towards AI🔎 Find similar documents

Explaining negative R-squared
When I first started out doing machine learning, I learnt that: * R² is the coefficient of determination, a measure of how well is the data explained by the fitted model, * R² is the square of the coe...
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents
Comprehensive Guide on R-squared
R-squared ( $R^2$ ) is a popular performance metric for linear regression to assess the model's goodness-of-fit. There are two equivalent interpretations of $R^2$ : $R^2$ captures how much of the tota...
📚 Read more at Skytowner Guides on Machine Learning🔎 Find similar documents

Explained vs. Predictive Power: R², Adjusted R², and Beyond
1 Introduction You trust R². Should you? You proudly present a model with R² = 0.95. Everyone applauds. But what if your model fails miserably on the next new data? When building a statistical model, ...
📚 Read more at R-bloggers🔎 Find similar documents

Negative R2: Where Did You Go Wrong?
A statistical example Continue reading on Towards Data Science
📚 Read more at Towards Data Science🔎 Find similar documents


