Serialization&Deserialization Java

Basic Serialization in Java
What is Serialization Serialization is the process of converting an object’s state (including its references) to a sequence of bytes, as well as the process of rebuilding those bytes into a live objec...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Serialization
Versions [{“Name”:“Java SE 1.1”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 1.2”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 1.3”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 1.4”,“GroupName”:null},{“Name”:“Java SE 5”,“GroupName...
📚 Read more at Essential Java🔎 Find similar documents

Java Serialization: Day 14 — Exploring Object Serialization in Java
Welcome to Day 14 of our 30-Day Java Challenge! Today, we’re going to explore Java Serialization, a mechanism of converting an object into a byte stream, which can be persisted to a file or transferre...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Secure Coding in Java: A Practical Guide to Avoiding Deserialization Flaws
You can read the full story for free by clicking here Introduction Java serialization and deserialization provide a convenient mechanism to convert objects to a byte-stream representation (serializati...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents
On Lambdas, Anonymous Classes and Serialization in Java
Serialization in Java is a mechanism by which objects can be marshaled to and from streams of bytes, allowing them to be sent in sockets or stored in files, for instance. As an example, consider a…
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents
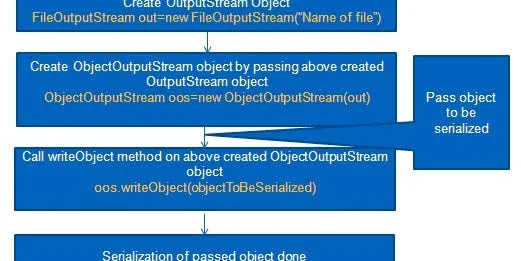
Complete guide to serialization in java
Java provides mechanism called serialization to persists java objects in a form of ordered or sequence of bytes that includes the object’s data as well as information about the object’s type and the t...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Record Serialization - Sip of Java
Learn about Records Serialization… Records, introduced in Java 16 (JEP 395) , address several key issues related to serialization. A source of frequent headaches in the Java ecosystem. Transparent Dat...
📚 Read more at Inside Java🔎 Find similar documents

Serialization Filters - Sip of Java
Serialization Filters were added in JDK 9 (see JEP 290 ) and updated in JDK 17 (see JEP 415 ). Serialization filters give Java applications more control over how incoming data is deserialized. Let’s l...
📚 Read more at Inside Java🔎 Find similar documents

Understanding Jackson Serialization, Deserialization, and Spring Boot Custom Jackson Modules
What is Jackson Serialization? Serialization is the process of converting a Java object into a JSON string. This is useful when you want to send Java objects over the network, save them to files, or i...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Monitoring Deserialization to Improve Application Security
Many Java frameworks rely on serialization and deserialization for exchanging messages between JVMs on different computers, or persisting data to disk. Monitoring deserialization can be helpful for ap...
📚 Read more at Inside Java🔎 Find similar documents

Serialization 2 0: A Marshalling Update!
Almost three decades have passed since the creation of Java Serialization—a feature which is widely frowned upon—and application requirements for externalization of objects have changed significantly...
📚 Read more at Inside Java🔎 Find similar documents

Serialization - A New Hope
Almost three decades have passed since the creation of Java Serialization—a feature which is widely frowned upon—and application requirements for externalization of objects have changed significantly...
📚 Read more at Inside Java🔎 Find similar documents


