Websockets
WebSockets
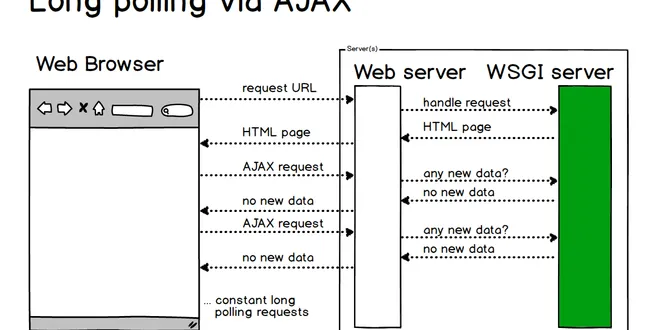
WebSockets are a protocol for full-duplex web communications. Learn about WebSockets on Full Stack Python.
📚 Read more at Full Stack Python🔎 Find similar documents
WebSockets
WebSockets You can use WebSockets with FastAPI . WebSockets client In production In your production system, you probably have a frontend created with a modern framework like React, Vue.js or Angular....
📚 Read more at FastAPI Documentation🔎 Find similar documents
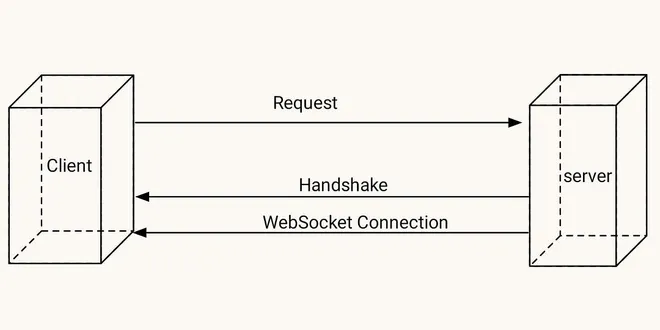
Understanding WebSocket in depth
What the heck is WebSocket? WebSockets enable bidirectional, real-time communication over a single, long-lived connection. Unlike HTTP, which follows a request-response model, WebSockets allow the se...
📚 Read more at Javarevisited🔎 Find similar documents

Getting Started With Node.js and WebSockets
WebSockets are the edgy younger sibling of http. They let you maintain an open connection for real time updates. Let’s make a simple chatroom that just displays messages from users. To keep this…
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

WebSockets in Go and GoFr
The Evolution of Real-Time Communication: A Brief History In the early days of web development, achieving real-time communication between clients and servers was a challenge. Developers had to rely o...
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

Building Real-time Applications: A Look into WebSockets with Spring
WebSockets is an advanced technology that makes it possible to open an interactive communication session between a user’s browser and a server. With this API, you can send messages to a server and rec...
📚 Read more at JavaToDev🔎 Find similar documents

WebSockets in iOS Using Swift
WebSockets allow for extremely fast two-way networking communication, which lets you send and receive updates quicker and more often, not to mention securely. WebSocket is a communication protocol…
📚 Read more at Better Programming🔎 Find similar documents

Node.js and Websockets on AWS
On some projects, we need the client to be able to communicate with the server in real-time. The Websocket protocol works over the TCP socket connection and provides the ability of real-time…
📚 Read more at Better Programming🔎 Find similar documents

Asyncio WebSocket Clients
Websockets provide a full-duplex way for clients and servers to communicate on the web. It is an efficient and widely used protocol for real-time applications like chat, games, and streaming of text, ...
📚 Read more at Super Fast Python🔎 Find similar documents
High resilience with Web Sockets
In a fast-moving world with huge data volume, WebSockets tend to come out as the first option when talking about real time communications, hence, the importance to improve their capabilities when…
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents
Managing WebSocket Connections in Distributed Systems: A Real-World Solution
The Problem of the Disappearing WebSocket Messages Last month, our team faced a puzzling issue. Users would click a button in our app, but sometimes nothing would happen — no error, no response, just ...
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents
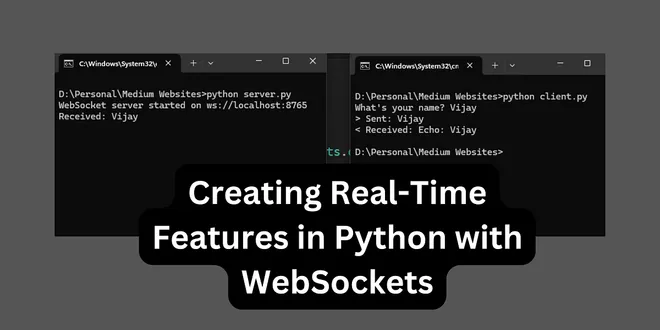
Creating Real-Time Features in Python with WebSockets
A Relatable Beginning: Over a Chai Moment Let me tell you something funny. Not long ago, I was working on a hobby project — a live chat app. I wanted messages to appear instantly, but everything seeme...
📚 Read more at Python in Plain English🔎 Find similar documents


