numbers Python
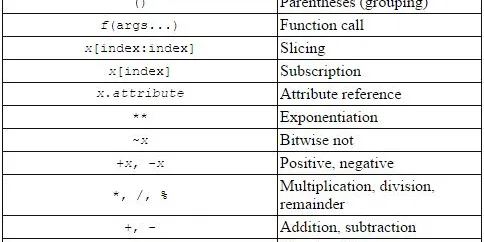
Python Numbers
This data type supports only numerical values like 1, 31.4, -1000, 0.000023, 88888888.Python supports 3 different numerical types. int - for integer…
📚 Read more at ThePythonGuru🔎 Find similar documents
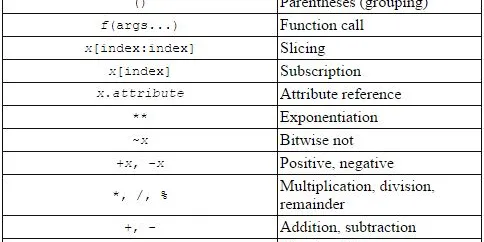
Python Numbers
This data type supports only numerical values like 1, 31.4, -1000, 0.000023, 88888888.Python supports 3 different numerical types. int - for integer…
📚 Read more at ThePythonGuru🔎 Find similar documents
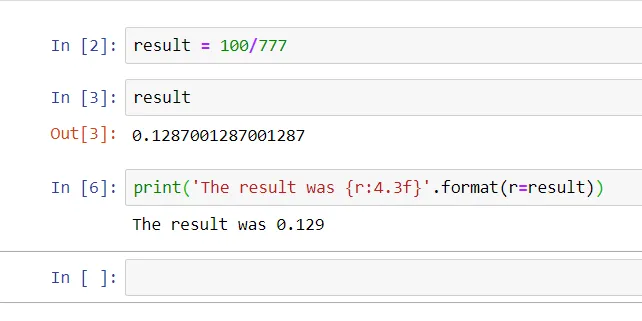
Day 4: Numbers in Python
Something great picked up after reading about Numbers in Python. The number can be a whole number ( int), a number with decimal (), a float using scientific notation, with e indicating the power of…
📚 Read more at Analytics Vidhya🔎 Find similar documents

Python Useful Tips — Best Practices for Using Numbers and Strings
Numbers serve as the fundamental data type in nearly all programming languages, serving as the building blocks that enable us to interact with the tangible world through code. Python, in particular…
📚 Read more at Python in Plain English🔎 Find similar documents

1.3 Numbers
This section discusses mathematical calculations. Types of Numbers Python has 4 types of numbers: Booleans Integers Floating point Complex (imaginary numbers) Booleans (bool) Booleans have two values:...
📚 Read more at Practical Python Programming🔎 Find similar documents

What Is Up With The Numbers In Python
Let’s uncover why the size of an integer in Python is at least 24 bytes Continue reading on Better Programming
📚 Read more at Better Programming🔎 Find similar documents

3 Things You Might Not Know About Numbers in Python
If you’ve done any coding in Python, there’s a good chance that you’ve used a number in one of your programs. For instance, you may have used an integer to specify the index of a value in a list. But…...
📚 Read more at Python in Plain English🔎 Find similar documents

Unlimited Creativity: Unleashing the Power of Numbers and Strings in Python
N umbers are the most basic data type in almost all programming languages, and they form the foundation for connecting the real world through code. In Python, there are three types of numerical values...
📚 Read more at Level Up Coding🔎 Find similar documents

How Python Achieves Infinitely Large Numbers
Python is one of the easiest programming languages ever created, yet rich of high-level features, which make it very appealing to beginners and experts alike. As an amateur compiler developer, I love ...
📚 Read more at Python in Plain English🔎 Find similar documents
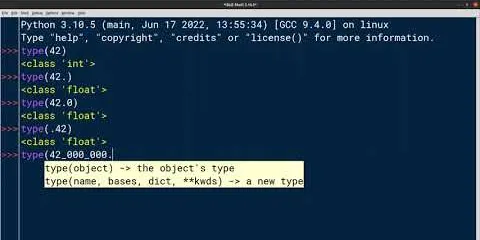
Introduction to Integers and Floating Point Numbers: Python Basics
This video is an introduction to working with integers and floating point numbers in Python. Math and computer programming aren’t as correlated as some people might believe, numbers are an integral pa...
📚 Read more at Real Python🔎 Find similar documents

4 Python Number Things I Wish I Knew Earlier
Working with numbers in Python seems straightforward — until you trip over the little quirks hiding under the surface. Over the years, I’ve learned that a few “tiny details” can make a huge difference...
📚 Read more at Python in Plain English🔎 Find similar documents

Numbers and Math Practice: Python Basics Exercises
This is a preview of Python Basics Exercises: Numbers and Math video course. In this hands-on course, you’ll have the opportunity to reinforce your understanding of numbers and math in Python programm...
📚 Read more at Real Python🔎 Find similar documents


